The surgical extraction techniques for single-rooted and multi-rooted teeth are similar, and include the following steps:
- Creation of a flap.
- Removal of bone and exposure of an adequate part
of the root. - Extraction of the tooth or root with elevators or forceps.
- Postoperative care of wound and suturing.
The surgical extraction involves teeth with intact crowns, roots and root tips, and presents specific characteristics in each of these cases
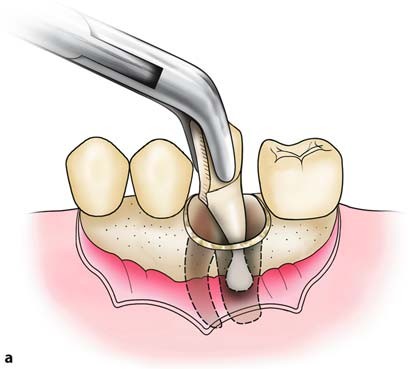
Extraction of Multi-Rooted Tooth
The removal of a single-rooted or multi-rooted tooth with an intact crown is achieved with the simple extraction technique and is usually very easy. There are certain situations, though, when the extraction requires a surgical approach, to avoid undesirable complications. The procedure for these cases is as follows.
When the removal involves a multi-rooted Maxillary tooth, an envelope flap is created, and the buccal plate is removed using a round bur, as far as the root bifurcation. The two oral roots are sectioned after a groove is created using a fissure bur, and the crown, together with the palatal root, is then removed. The two other sources are then removed separately, preferably using a straight elevator or root tip forceps.

Steps in the surgical extraction of an intact maxillary first molar. Reflection of the envelope flap, sectioning of two buccal roots from the crown, removal of the crown together with the palatal root, and then finally removal of the mesial and distal roots
Extraction of an Intact Tooth
with Hypercementosis of the Root Tip
If an extraction is indicated for a tooth that has hypercementosis at the root tip, then it must be performed using the surgical technique. Otherwise, as already mentioned, the fracture of the root tip is inevitable. The procedure used for such cases generally is described below:
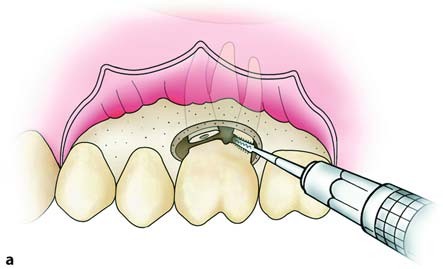
When the tooth to be extracted is single-rooted, an L-shaped flap is initially created, and the bone covering the buccal surface of the root is then removed. The extraction is performed easily towards the oral side that is no longer covered by bone, using forceps or elevators.
Diagrammatic illustrations are showing the steps in the surgical extraction of a single-rooted tooth with hypercementosis at the root tip. An L-shaped incision is made, and the flap is reflected. The buccal plate covering the surface of the root is removed, and the tooth is extracted using forceps.



